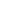فيما يتعلق بالديسيبل وdBm وdBi
يقدر بـ 15 دقيقة لإنهاء القراءة
دي بي (ديسيبل)
DB هي وحدة نسبية تستخدم لتمثيل النسبة بين كميتين. وعادة ما يستخدم لوصف نسبة الطاقة أو الجهد (أو التيار).
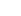
التعريف: (dB=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P_2} {P_1} \ right)) أو (dB=20 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {V_2} {V_1} \ right) )
من بينها، (P_1) و (P_2) هما قيمتان للطاقة، و (V_1) و (V_2) هما قيمتان للجهد أو التيار.
ملحوظة: الديسيبل هي وحدة نسبية تمثل النسبة بين كميتين، وليست قيمة مطلقة.
1. صيغة حساب الديسيبل لنسبة الطاقة:
عند مقارنة قيمتين للطاقة، فإن صيغة حساب الديسيبل هي:
DB=10log10 (P1P2)، حيث (P_1) هي القدرة المرجعية (عادةً قيمة ثابتة)، و(P_2) هي القدرة المراد قياسها. إذا كانت (P_1) تساوي 1 واط، فيمكن تبسيط المعادلة أعلاه على النحو التالي: dB=10log10 (P2)، حيث (P_2) هي قيمة الطاقة بالواط.
2. صيغة حساب الديسيبل لنسبة الجهد (أو التيار):
عند مقارنة قيمتين للجهد (أو التيار)، فإن صيغة حساب الديسيبل هي:
ديسيبل = 20log10 (V1V2)
ربما
ديسيبل = 20log10 (I1I2)
من بينها، (V_1) و (I_1) هي الفولتية والتيارات المرجعية (قيم ثابتة عادة)، في حين أن (V_2) و (I_2) هي الفولتية والتيارات المراد قياسها. إذا كان (V_1) أو (I_1) يساوي 1 فولت أو 1 أمبير، فيمكن تبسيط الصيغة أعلاه على النحو التالي:
ديسيبل = 20log10 (V2)
ربما
ديسيبل = 20log10 (I2)
Here (V_2) and (I_2) are voltage and current values in volts or amperes.
Note: In these formulas, (\ log_ {10}) represents the logarithm based on 10. If (P_2/P_1) or (V_2/V_1) (or (I_2/I_1)) is greater than 1, then the decibel value is positive; If it is less than 1, the decibel value is negative. The larger the decibel value, the greater the multiple of (P_2) relative to (P_1) (or (V_2) relative to (V_1), or (I_2) relative to (I_1)).

DBm (decibels milliwatts)
DBm is an absolute unit used to represent power values, with a reference point of 1 milliwatt (0.001 watt).
Definition: (dBm=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P} {1mW} \ right))
Where (P) is the power value to be measured.
For example, if the power of a signal is 1 watt, then its power is (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30 dBm).
DBm is commonly used to describe the power of wireless signals or the sensitivity of receivers.
DBm calculation formula
dBm=10log10(1mWP)
Among them,
(P) is the power value to be measured, in milliwatts (mW).
(1mW) is the reference power value, which corresponds to the power of 0dBm.
Related information
1. Unit conversion:
0dBm corresponds to 1 milliwatt (1mW).
For every 3dBm increase, the power doubles; For every reduction of 3dBm, the power is halved.
For example, 30dBm corresponds to 1 watt (1W), because (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30) (because 1W=1000mW).
2. Common conversion values:
o 30dBm = 1W
o 40dBm = 10W
o 50dBm = 100W
3. Precautions:
DBm represents the absolute value of power, not the power ratio.
In the calculation, pay attention to the unit of power and ensure that it is consistent with the unit of reference power (1mW).
Example
If the power of a signal is 4 watts (4W), then its power (in dBm) can be calculated as follows:
dBm=10log10(1mW4000mW)=10log10(4000)=10*(3+log10(4))≈36.02dBm
(Here (\ log_ {10} (4) \ approx 0.602) is the base 10 logarithm of 4)
DBi (decibels relative to isotropy)
DBi is a unit used to describe antenna gain, with its reference point being an idealized isotropic antenna (i.e. an antenna that uniformly radiates or receives in all directions).
Definition: (dBi=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {G} {G_ {iso}} \ right))
Among them, (G) is the gain of the antenna to be measured, and (G_ {iso}) is the gain of an isotropic antenna (theoretically 1).
Note that since isotropic antennas do not exist in reality, dBi is a relative unit, but it provides a convenient reference point to compare the gains of different antennas.
DBi is commonly used to describe the gain of antennas used in wireless communication.
DBi calculation formula
dBi=10log10(E0E)
Among them:
(E) is the effective radiation power or gain of the actual antenna.
(E0) is the effective radiation power or gain of an ideal isotropic antenna. An ideal omnidirectional antenna has uniform radiation in all directions, and there is no such antenna in practice, so it serves as a reference benchmark.
Related information
1. المعيار المرجعي: المعيار المرجعي لـ dBi هو هوائي شامل الاتجاهات، وهو نموذج مثالي من الناحية النظرية يستخدم لمقارنة كسب الهوائيات الأخرى.
2. العلاقة مع dBd: dBi وdBd كلاهما وحدتان تصفان كسب الهوائي، لكن معاييرهما المرجعية مختلفة. المعيار المرجعي للديسيبل هو هوائي شامل الاتجاهات، في حين أن المعيار المرجعي للديسيبل هو هوائي ثنائي القطب
(هوائي ثنائي القطب). ومن المعتقد عمومًا أنه عند تمثيل نفس الكسب، تكون القيمة التي يمثلها dBi أكبر بمقدار 2.15 من القيمة التي يمثلها dBd (أي dBi=dBd+2.15).
3. مثال: إذا تم تمثيل كسب الهوائي على أنه 16dBd في dBd، فسيتم تمثيل كسبه على أنه 18.15dBi في dBi (عادةً ما يتم تجاهل المنازل العشرية، فهو 18dBi).
باختصار، dBi هي وحدة تستخدم لوصف كسب الهوائي، وتعتمد صيغة حسابها على نسبة قدرة الإشعاع الفعالة للهوائي الفعلي إلى قدرة الإشعاع الفعالة للهوائي المثالي متعدد الاتجاهات . بالمقارنة مع dBd، فإن مرجع dBi هو هوائي شامل الاتجاهات، لذلك عند تمثيل نفس الكسب، ستكون قيمة dBi أكبر بمقدار 2.15 من قيمة dBd.

















 ميمو .هوائي
ميمو .هوائي